Single-destination Mode
Single-destination mode is selected by choosing "single destination" from the destination mode drop-down box (see the screenshot below). Single destination mode allows you to specify one particular DS to which the VSP will be establishing its outgoing connections (when allowed by the routing mode and according to the connection mode option).
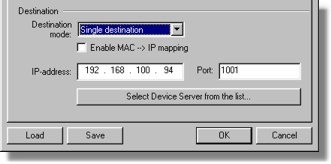
The destination DS can be specified either by its IP-address, or its MAC-address:
| • | When Enable MAC-->IP mapping optionbox is not checked the DS is specified by its IP-address. |
| • | When Enable MAC-->IP mapping optionbox is checked the DS is specified by its MAC-address. This option exists to make the VSP-to-DS communications independent of the IP-address of the DS. If the DS is running with DHCP enabled (DHCP (DH) setting is 1 (enabled)) the IP-address may eventually change but the MAC-address will remain the same. |
With mapping enabled, the VSP "discovers" current IP-address of the DS each time it needs to communicate with this DS. The process is illustrated by the following log in the Port Monitor :
12/17/03 17![]() 00 - COM3 (INFO): Port opened
00 - COM3 (INFO): Port opened
12/17/03 17![]() 06 - COM3 (INFO): MAC --> IP mapping for MAC 0.2.3.4.61.189...ok, mapped to 192.168.100.92
06 - COM3 (INFO): MAC --> IP mapping for MAC 0.2.3.4.61.189...ok, mapped to 192.168.100.92
12/17/03 17![]() 06 - COM3 (INFO): Established TCP connection with node 192.168.100.92:1001
06 - COM3 (INFO): Established TCP connection with node 192.168.100.92:1001
12/17/03 17![]() 29 - COM3 (INFO): TCP connection closed
29 - COM3 (INFO): TCP connection closed
12/17/03 17![]() 29 - COM3 (INFO): Port closed
29 - COM3 (INFO): Port closed
--- IP-address of the DS has changed ---
12/17/03 17![]() 03 - COM3 (INFO): Port opened
03 - COM3 (INFO): Port opened
12/17/03 17![]() 05 - COM3 (INFO): MAC --> IP mapping for MAC 0.2.3.4.61.189...ok, mapped to 192.168.100.91
05 - COM3 (INFO): MAC --> IP mapping for MAC 0.2.3.4.61.189...ok, mapped to 192.168.100.91
12/17/03 17![]() 05 - COM3 (INFO): Established TCP connection with node 192.168.100.91:1001
05 - COM3 (INFO): Established TCP connection with node 192.168.100.91:1001
In the above example the IP-address of the DS has changed between the "communications sessions" but the VSP was able to connect to the same DS by using the MAC-->IP mapping.
Because the VSP is using broadcast UDP communications to "find" the DS with matching MAC-address, the MAC-->IP mapping feature only works for local Device Servers, i.e. devices located on the same network segment* with the PC (running VSP ).
Also specified in the destination section of the VSP properties dialog is the port number on the DS. This must be the same number as the one specified in the Port Number (DP) setting of the destination DS.
Instead of entering the destination data manually, you can press the Select Device Server from the list... button and choose the DS from the list. The button brings up the dialog , similar to the main window of the DS Manager . In fact, it is the DS Manager , with the following two differences:
| • | There is an additional Select button. To select a particular DS as a destination for the VSP single-click on the DS in the device list and press Select. Alternatively, you can double-click on the DS in the device list. |
| • | There is no COM access mode available in the access mode drop-down box. This is because you are choosing a network destination for the VSP so the target DS has to be selected from the list of devices accessible through the network! |
When you select the DS from the list the VSP Manager selects or deselects the MAC-->IP mapping automatically:
| • | Mapping is deselected if the DS is not local (no matter the DS is running with DHCP enabled or disabled). |
| • | Mapping is deselected if the DS is local but is running with DHCP disabled. |
| • | Mapping is selected if the DS is local and is running with DHCP enabled. |
Additionally, when you select the DS from the list the destination port is set automatically to the one, defined by the Port Number (DP) setting of the selected DS.
* The definition of the network segment implies that there are only network hubs (and no routers, bridges, firewalls, etc.) between the PC and all other devices on the segment. Broadcast messages cannot pass through the routers and cannot reach the Device Servers located behind those routers.