#26, M1S: IR Command Processor
Function: Records and plays back infrared commands (codes) of conventional IR remote controls
Form factor: M1S
Category: Input/output module
Special needs: ---
Power requirements: 5V/100mA
See also: ---

Details
Tibbit #26 is an IR command processor that records and plays back the infrared commands of conventional IR remote controls. This Tibbit utilizes an FPGA-based circuit for capturing and reproducing IR signals, thus ensuring high timing precision and low signal jitter. Tibbit #26 is based on the iCE5LP1K-SWG36 FPGA from Lattice Semiconductor.
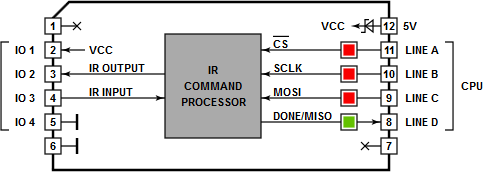
Tibbit #26 is controlled through the standard SPI lines: –CS, SCLK, MOSI, and MISO. There are two non-standard features built on top of SPI:
- The –CS and SCLK lines are used to produce a reset pulse for the FPGA IC.
- The MISO line also doubles as a status (DONE) line.
Both non-standard features are described in Resetting and Initializing the Onboard FPGA.
A suitable IR receiver and emitter must be connected to this Tibbit. Typically, you would pair Tibbit #26 with #20 or #21, then attach the IR receiver and emitter using wires. Tibbit #26 can work with a wide variety of IR receivers and transmitters. We have provided some examples of suitable IR front ends, but the spectrum of receivers and transmitters that will work with this Tibbit is much wider than what's documented here.
Note that there is no need to have a current-limiting resistor on the IR OUTPUT line. This is a current-regulated output that internally limits the output current to 500mA.
LEDs
There are three red LEDs and one green LED. These four LEDs are connected to the four interface lines of Tibbit #26. The LEDs light up for the LOW state of the interface lines.
The red LEDs are connected to the –CS, SCLK, and MOSI lines. The green LED is connected to the DONE/MISO line.
Sample Project
The use of Tibbit #26 is illustrated by a Tibbo BASIC test project. You can find it here: https://github.com/tibbotech/CA-Test-Tibbit-26.
 VCC output (IO 1) of this Tibbit is taken from the 5V rail of the TPS. When heavy loads are placed on the VCC output, the current draw from the TPS 5V rail can increase significantly. Therefore, make sure you use a reliable power Tibbit or another robust method of powering the TPS to avoid any power dips. For the same reason, caution should be taken when using multiple instances of this Tibbit on a single TPS board.
VCC output (IO 1) of this Tibbit is taken from the 5V rail of the TPS. When heavy loads are placed on the VCC output, the current draw from the TPS 5V rail can increase significantly. Therefore, make sure you use a reliable power Tibbit or another robust method of powering the TPS to avoid any power dips. For the same reason, caution should be taken when using multiple instances of this Tibbit on a single TPS board.
Further Info
- Theory of operation
- Resetting and initializing the onboard FPGA
- SPI read and write transactions
- Registers
- Examples of wiring to IR receivers & emitters
