Connectivity Settings
OSS currently supports two communication methods: Wi-Fi and cellular.
Configuration Options
Users can select one of three network connectivity options:
- Wi-Fi: The device connects only via Wi-Fi.
- Cellular: The device connects via cellular only. See SIM Card Installation.
- Wi-Fi with Cellular Backup: The device primarily uses Wi-Fi but switches to cellular if Wi-Fi fails. Please see the following section for further details.
Wi-Fi with Cellular Backup
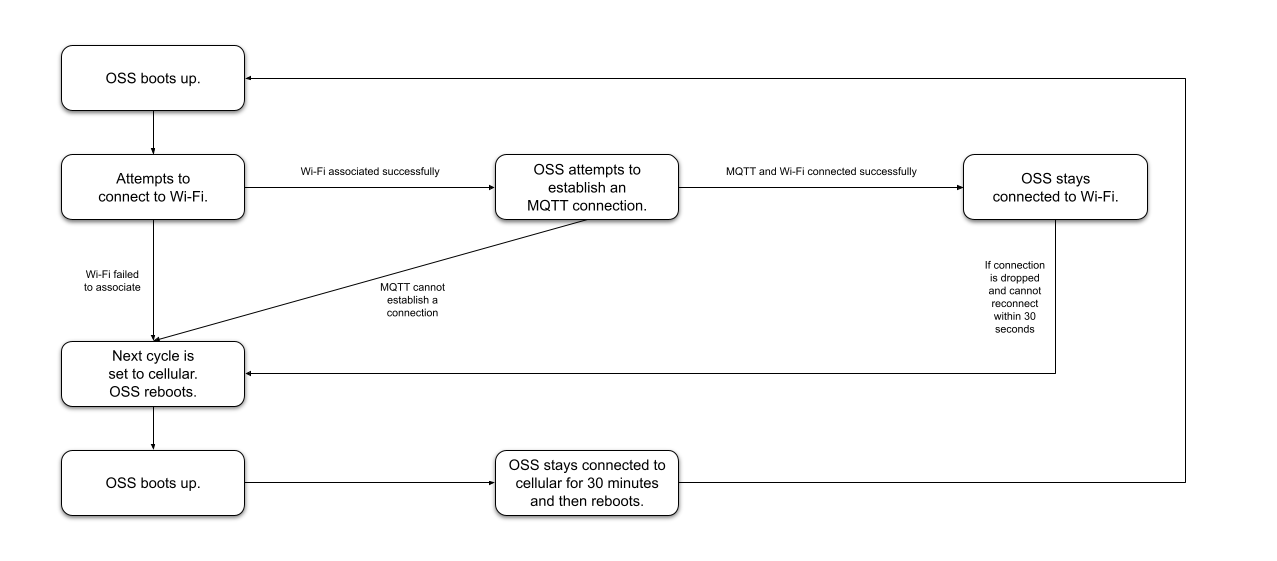
The Wi-Fi with Cellular Backup mode enables automatic fallback to cellular when Wi-Fi communication fails. This is particularly useful for applications where redundancy is critical, ensuring uninterrupted data transmission. While in this mode, sensor sampling and remote firmware upgrades operate as usual.
What Constitutes a Wi-Fi Failure?
Wi-Fi failures can be categorized into two main scenarios:
- Association Fails:
- The Access Point (AP) is unavailable
- The device attempts to associate with the AP but fails
- Data Connection Fails:
- DHCP fails
- The AP is available but does not provide a data connection
- The AP does not provide sufficient bandwidth
- The device gets disassociated
- MQTT connection drops
Low-Power and Always ON Modes
Wi-Fi with Cellular Backup operates differently in Low-Power Mode and Always ON Mode:
Low-Power Mode
If Wi-Fi fails during a transmission cycle, the device does not immediately switch to cellular to preserve battery life. Instead, it flags the next cycle to use cellular.
Note: Maximum Awake Time is set to 3 minutes when in Wi-Fi with Cellular Backup mode.

Always ON Mode
If Wi-Fi fails, the device immediately reboots and switches to cellular. It remains on cellular for 30 minutes, after which it reboots again and attempts to reconnect to Wi-Fi. This minimizes cellular data usage if Wi-Fi recovers within the 30-minute window.