Ethernet Lines and Jack/Magnetics Data
Pin Functions and Descriptions
|
Pin Number |
Signal Name |
Direction |
Description |
|
Mag. conn., #1 |
RX+ |
Input |
Ethernet port, positive line of the differential input signal pair |
|
Mag. conn., #2 |
RX- |
Input |
Ethernet port, negative line of the differential input signal pair |
|
Mag. conn., #9 |
TX+ |
Output |
Ethernet port, positive line of the differential output signal pair |
|
Mag. conn., #10 |
TX- |
Output |
Ethernet port, negative line of the differential output signal pair |
|
Mag. conn., #11 |
AVCC |
Output |
"Clean" 1.8V power output for magnetics circuitry |
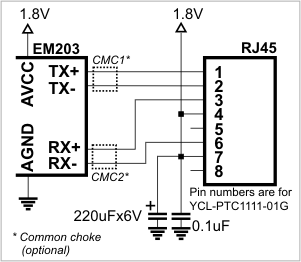
The EM203's Ethernet port supports the 10/100BaseT standard. However, the module does not include built-in Ethernet magnetics. Therefore, external magnetics circuitry must be connected to the TX+, TX-, RX+, RX-, and AVCC pins. The AVCC pin provides clean, noise-sensitive power for the magnetics circuitry, with an output voltage of 1.8V.
EMI Reduction
To reduce electromagnetic interference (EMI), you may optionally add common-mode chokes to the TX and RX lines. When properly selected, these chokes will have minimal impact on the "useful" Ethernet signals but can significantly reduce unwanted EMI.
 Do not connect the AVCC and VCC pins together.
Do not connect the AVCC and VCC pins together.
Doing so will cause permanent damage to the EM203.
Placement on the Host PCB
One way to mount the EM203 on the host PCB is shown in the diagram below:
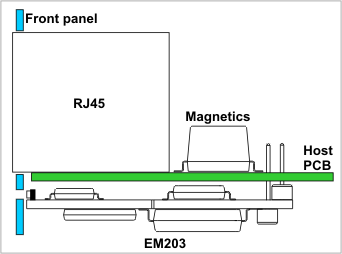
- The EM203 is installed on the bottom side of the host board.
- A standard RJ45 jack and the magnetics circuitry are placed on the top side of the board. Alternatively, you can use an RJ45 jack with integrated magnetics.
In this configuration, the EM203 minimizes board space usage, and its LEDs are positioned near the host device’s front panel. A small opening or window in the housing of the host device allows the LEDs to be visible from the outside.
Another approach is to combine the EM203 with the RJ203 jack/magnetics module. Please refer to Ordering and Specifications for the part numbers to order the combination.
