Serial Port and General-Purpose I/O Lines
Pin Functions and Descriptions
|
Pin Number |
Signal Name |
Direction |
Description |
|
#16 |
TX |
Output |
Serial transmit line |
|
#15 |
RX |
Input |
Serial receive line |
|
#18 |
P5 (RTS/DIR) |
Input/output (output) |
General-purpose input/output line Request to send output (full-duplex mode) Data direction control output (half-duplex mode) |
|
#17 |
P4 (CTS/SEL) |
Input/output (input) |
General-purpose input/output line Clear to send input Full-/half-duplex selection input |
|
#20 |
P3 (DTR) |
Input/output (output) |
General-purpose input/output line Data terminal ready output |
|
#19 |
P2 (DSR) |
Input (input) |
General-purpose input line Data set ready input |
|
#13 |
P1 |
Input/output |
General-purpose I/O line |
|
#12 |
P0 |
Input/output |
General-purpose I/O line |
Line functions defined by the Application Firmware are shown in blue.
The EM100 features:
- A serial port (RX and TX lines).
- Several general-purpose I/O lines (P0–P5).
All these lines are of CMOS type. From a hardware perspective:
- P0–P5: General-purpose I/O lines can function as inputs or outputs, except for P2, which can only work as an input.
- The maximum load current for each I/O line is 10mA.
Structure of I/O Lines
The simplified structure of the EM100's I/O lines is shown in the circuit diagram below.
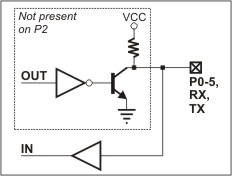
The EM100's I/O lines exhibit a quasi-bidirectional nature, functioning like open-collector outputs with a weak pull-up resistor. These lines lack explicit direction control, as their behavior is determined by the application. For instance, to measure an external signal applied to a pin, the OUT line should be set to HIGH. Additionally, it is safe to externally drive the pin LOW even when it is internally set to HIGH.
Firmware-Dependent I/O Functionality
The EM100's Application Firmware maps certain serial port functions onto the general-purpose I/O pins.
These mappings are shown in blue in the table at the top of this topic, for example:
- P5 functions as a universal input/output pin by default, but firmware can configure it as the RTS (Ready To Send) output of the serial port. Therefore, depending on the application, it can serve as either a general-purpose I/O line or a specific serial port control line such as RTS.
The actual functionality of the I/O lines is firmware-dependent. For additional details, refer to the documentation sections on Serial Port and Serial Communications.
CMOS-Type Compatibility
As a CMOS device, the EM100's serial port and I/O lines can be directly connected to the corresponding pins of most microcontrollers or microprocessors.
To connect the EM100 to a "true" serial port (e.g., the COM port of a PC), you must add an external interface IC, such as:
- MAX232 for RS232.
- MAX485 for RS485.
Logical Signal Behavior
The logical signals on the EM100's serial port lines are active LOW and behave as follows:
- TX and RX lines:
- HIGH when idle.
- LOW for the start bit.
- HIGH for the stop bit.
- CTS and RTS lines:
- LOW indicates "transmission allowed."
- HIGH indicates "transmission not allowed."
These signaling conventions are standard for CMOS-level serial ports and are the opposite of RS232 signaling. The inversion occurs because interface ICs (e.g., MAX232) also invert the signals internally.
