Transport Protocol & Listening Ports
On this step you select the protocol that will be used for exchanging the data between the Device Servers. You also choose the listening port number of the side(s) of the link that will be receiving incoming connections.
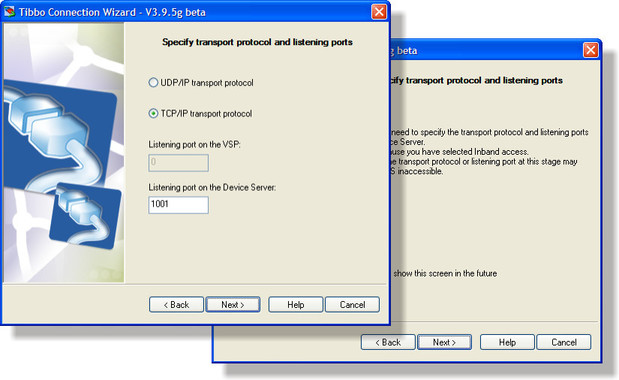
In general, we recommend you to stick to the TCP/IP, unless you have a good reason (which is very rare!) why you have to use UDP/IP protocol.
There is one case when the UDP/IP selection is not available and the TCP protocol is pre-selected for you- this is when you have specified an inband access method on the DS #2 step of the Wizard . Since inband access requires a TCP/IP data connection with the DS you must use TCP/IP transport protocol, or the configuration PC won't be able to access the DS #2 in the future.
Under What Circumstances Transport Protocol & Port Selection Is Disabled
As noted above, when you use Inband access mode for the wizard, you must use TCP/IP as the transport protocol. Also, port selection will be disabled in this case. At this stage of the Connection Wizard you are already in communication with a DS. The communication is done via the data transport channel of the DS (as opposed to a separate command channel, like in Telnet or out-of-band mode).
The DS is usually far away (somewhere on a WAN), otherwise you would not use inband access to reach it. Thus, there are all sorts of firewalls and gateways between yourself and the DS. Firewalls only allow traffic on certain ports to go through, and UDP packets are often dropped on WANs.
If you change the protocol to UDP now, or change the listening port on the DS, you may render it completely inaccessible. The change will occur, because the Wizard is in communication with the DS (on the proper port which you configured in the beginning). But at the end of the Wizard run, you'll have an unpleasant surprise - the DS may suddenly disappear.
Thus, when selecting Inband Access mode in the beginning of the Wizard, you cannot later change the Transport Protocol or Listening Port.
Listening ports
This screen also provides an option of entering the port number on the listening side(s) of the DS-to-DS link. By now the Wizard has already decided which side opens the connections . Connecting side needs to know the number of the listening port on the other side. For example, if it is the DS #1 that will always be connecting to the DS #2, then you only have to specify the listening port on the DS #1 side. Consequently, the listening port on the DS #2 textbox will be enabled, and the listening port on the DS #1 textbox will be disabled. If both sides will need to establish the connection, then you have to specify the listening ports on both sides too, and both textboxes will be active.
There is one case when the listening port on the DS #2 side is fixed and pre-selected for you- this is when you have specified an inband access method for this DS. In this case you have already specified the listening port (as the access port) on the DS #2 step of the Wizard (listening port and the access port are the same for inband mode).
Once the listening port on one side is known, the Wizard sets the destination port on the other side accordingly. If the DS #1 will need to connect to the DS #2 the Destination Port (DP) setting on the DS #1 will be the same, as the value of the Port Number (PN) setting on the DS #2 side. Likewise, if the DS #2 will have to connect to the DS #1 the Destination Port (DP) setting on the DS #2 will be the same as the Port Number (PN) setting on the DS #1.
ration for both connection directions, so the Destination Port on one side will point at the Porn Number on the other side.
How the listening port numbers are chosen
You can choose any port numbers of your liking, except the 65535. This is because 65535 is a special command port. What the Wizard is showing you by default is the default value of the Port Number (PN) setting of the DS on the receiving end of the connection (1001).
The only reason to change suggested port numbers is if your network's firewall bans most of the traffic so only specific ports are opened for communications. In this case you may need to adjust the port numbers to the requirements of your network.